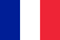
The valgus deformation of the thumb of the foot is the most frequent acquired deformation of the foot, which is characterized by the deviation of the thumb outward.
Pathology is bilateral in nature, mainly affects women over 35 years old.In most cases, the deformation is accompanied by chronic inflammation of the joint bag and deforming arthrosis of the plusnephalang joints, Pronational deviations of the first metatarsal bone.
Causes of the disease.Why is it dangerous?
The etiological causes of Valgus deviations of the thumb of the foot have not yet been fully studied.There are several theories of occurrence:
- Vestigial Theory.In the middle of the 19th century, it was believed that only models were subject to this deformation due to the use of model shoes in high -heeled, but during the study this pathology was found in men who wore flat -sole shoes.
- The theory of primary muscle weakness - was refuted in a detailed study of the problem.
- The theory of weakness of the ligamentous apparatus and the lack of aponeurosis of the sole - most scientists adhere to this theory.
There are a number of factors leading to the debut of this pathology:
- Excess weight increasing the load on the feet.
- Age -related dystrophic changes in the ligamentous articular apparatus.
- Weekens of heeled shoes are more than 5 cm, narrowed to the toe.
- The existing deformations of the skeleton (scoliosis, valgus deformation of the femoral and knee joints, flat feet).
The danger of pathology lies in the fact that over time this deformation leads to deformation of posture, it is possible to develop dystrophic-depths of the spine, hip and knee joints due to improper distribution of loading during walking, and injury to the muscles of the foot is accompanied by constant pain, which significantly worsens the well-being of a person.
Clinical manifestations
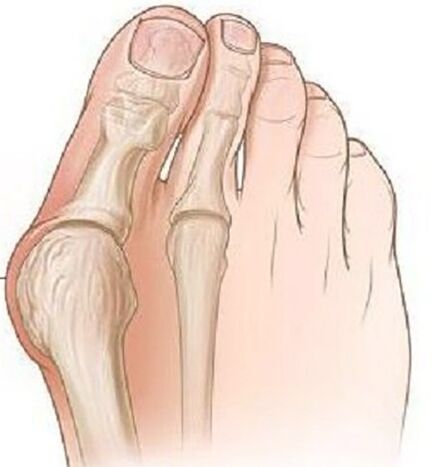
At the beginning of the disease, the valgus deformation does not show itself clinically.Most women are more concerned about the appearance of the foot-an increase in the metacarpal-phalanx joint and the outburst of the first finger becomes noticeable.
Over time, pain occurs, first when wearing narrow shoes and prolonged walking, and later the pain begins to be constant, aching.
Due to the improper distribution of weight, the limb, by the first and second finger on the sole, are formed by corns, the second finger is raised up, heavily extended, the “malleus” fingers are formed, which greatly complicates walking.Due to the deterioration of blood circulation and innervation in the anterior part of the foot, arthrosis and chronic bursitis develops.
Diagnostics
- During an objective examination, classical deformation with Valgus deviations of the thumb is visible, the distal part of the foot was expanded.In the projection of the head of the first metatarsal bone, there are signs of Bursite - hyperemia and edema of the skin, pain during palpation.
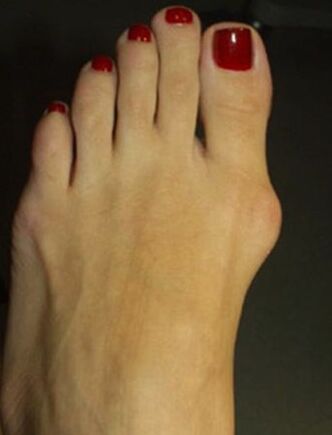
- The radiography of the foot in two projections.The front projection determines the degree of the thumb, the state of the metacarpal-phalanx joint, the degree of displacement of the sesamoid bone, and in the lateral projection the degree of flat feet is visualized and calculated, which very often occurs with Valgus deviations of the first finger of the foot.
- Plantography.On the print of the foot, made on paper, a line is drawn through the center of the heel and between the fourth and third fingers, the outer set of the foot is figuratively formed, according to which the presence of flattening of the foot and its degree are evaluated.In these patients, a flattened foot or flat feet of the 1st degree is more often detected.
Treatment and prevention
Depending on the severity of the process, conservative or surgical treatment is carried out.
Conservative treatment is carried out at the mild stage of the disease, various types of orthopedic insoles are used, which are selected individually and bring the deformed finger to the normal position, while the load on the front side of the limb is stabilized and distributed.
In children's and senile age, transverse bandaging of the distal limb with a laying between the first and second finger is used.To reduce pain, warm baths with sea salt and soda are used, radon baths give a good result.
To combat bursitis, local anti -inflammatory gels, compresses with dimexide and lidocaine are used, and with pronounced pain, novocaine blockade and intraarticular injections of glucocorticoids are used.
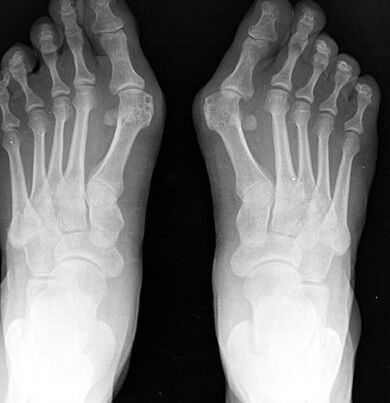
Surgical treatment is possible at any stage of the disease, it is carried out under local anesthesia, which reduces the list of contraindications for surgery.
At the 1st stage, the bone-cold growths are removed on the inner edge of the bone, while it is only possible to reduce the pain of the process, but not to prevent the development of deformation in the future.
With a severe deviation of the finger with the presence of flat feet, an osteotomy is carried out at the base of the plus bone of the first finger using a bone blade to reject the finger to the normal position, with the help of a lavsan tape, the transverse ligament of the sole is formed.After surgery, the leg is tightly fixed with a bandage for 4 weeks, it is recommended to use individual orthopedic insoles during the year.
Prevention of the disease is to use comfortable shoes without high heels, shoes should sit on the leg freely, a narrowed toe should not bring discomfort in the thumb.If there are any deformations of the skeleton, it is recommended to undergo preventive examinations at the orthopedist in order to identify and slow down the progression of the valgus deformation of the thumb of the foot.
Consequences and complications
A complication of the process is the development of Deichländer or “march” of the foot, which is characterized by acute pain, due to the microcracks in the pairing joints of the foot and tendovaginitis.
Due to the constant inflammatory process and mechanical damage, there is a risk of developing malignant neoplasms of the bone.